All chemical reaction can be explained in terms of atoms. It is important to understand the atomic structures of each elements.
The mass of an atom is concentrated in its minute positively charged nucleus.
- The atom consists of the three subatomic particles:
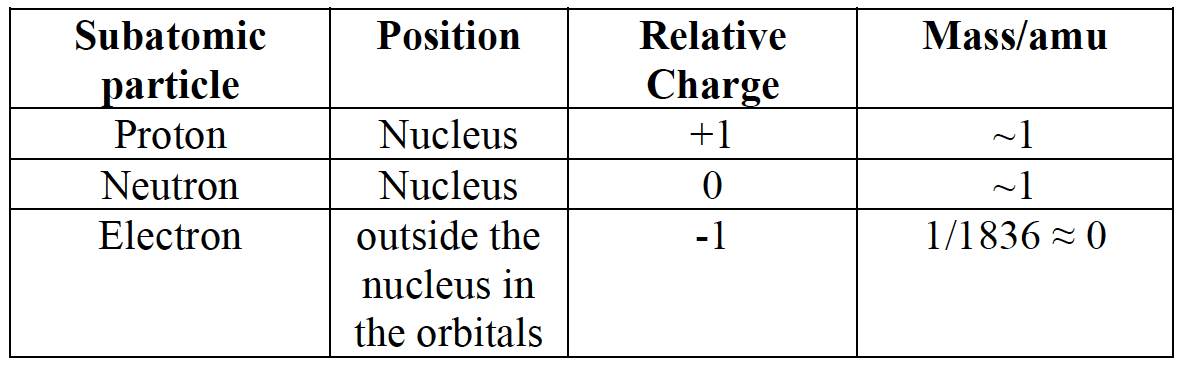
- The atomic number, $\bf Z$, is defined as the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom. It is also the number of electrons in a neutral atom
- The mass number, $\bf A$, is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in the nucleus as both contribute to the overall mass of the atom.
- Isotopes are different atoms of the same element with a different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. All isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties but may have different physical properties. Isotopes can be identified using the symbol; $\bf ^A_ZX$ where $\rm X$ is the chemical symbol for the element. The number of neutrons $\rm = A – Z$.
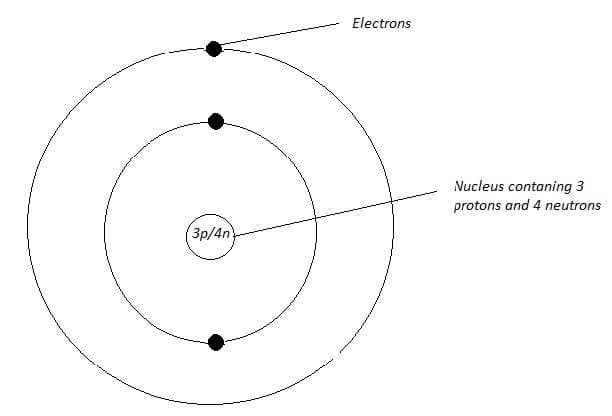
A simple model of a lithium atom 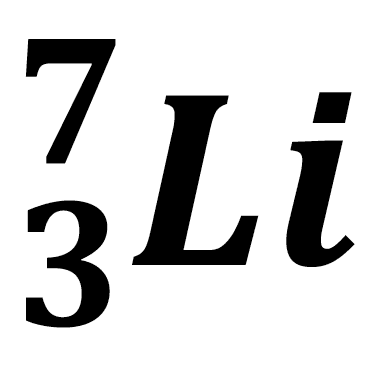
- As elements are made from a mixture of isotopes the mass of an average atom is given in the Periodic Table. This is the relative atomic mass.
Mass spectra
- The mass spectrometer is an instrument that determines the mass of individual atoms, molecules or ions.
- A mass spectrum of an element shows the number of isotopes and their relative abundance. This data can be used to find the relative atomic mind of an element.
 Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
