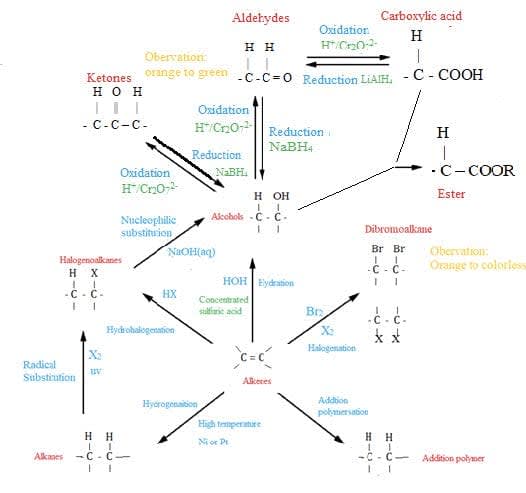
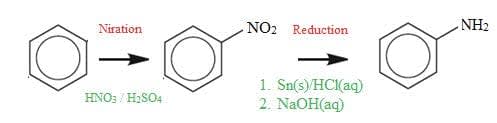
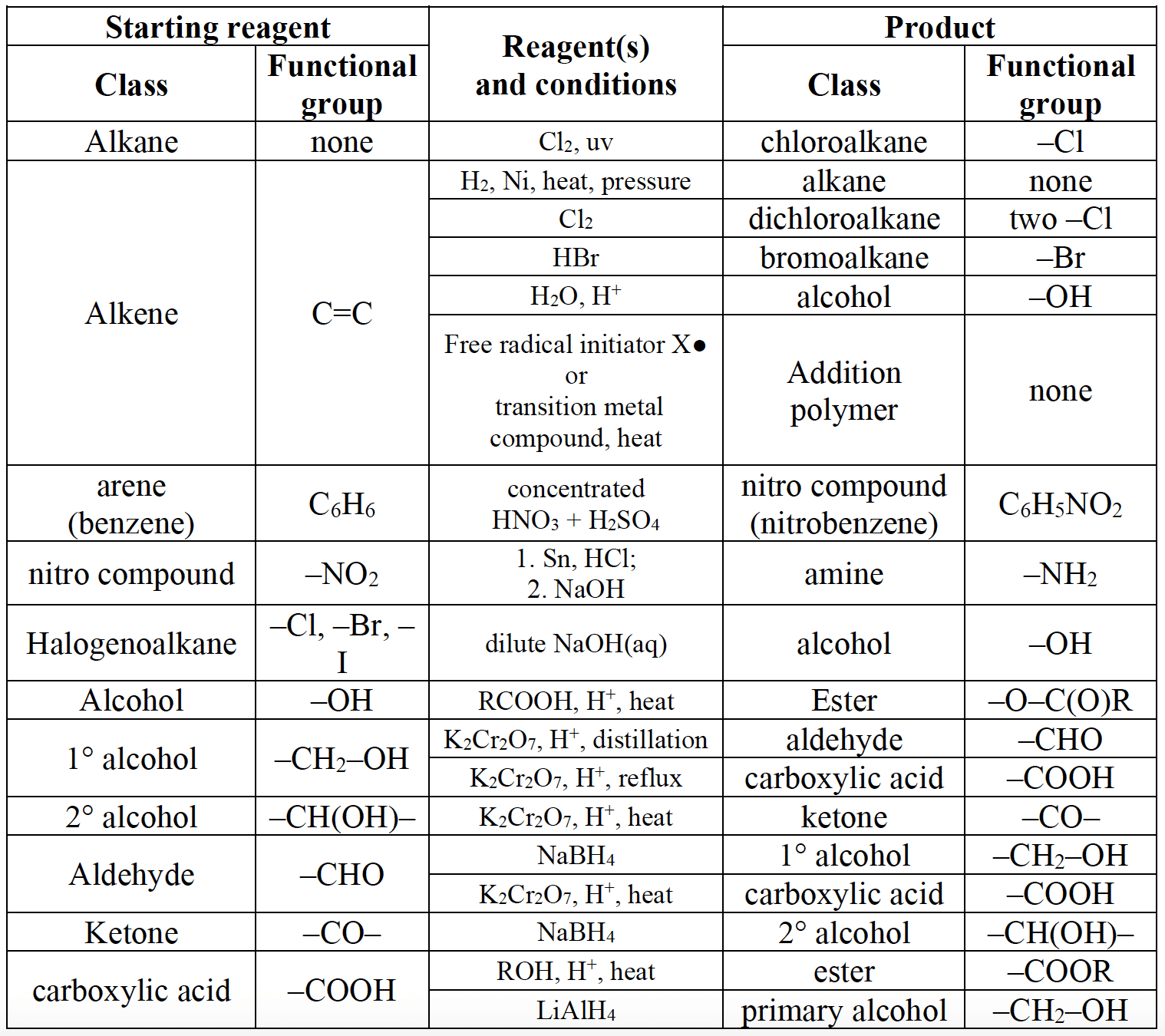
Organic synthesis is the systematic preparation of a compound from a widely available starting material or the synthesis of a compound via a synthetic route that often can involve a series of different steps.
- Organic chemistry often involves converting an available starting material into a required product in a multistep process.
- Retro-synthesis involves working backwards from a desired product, and deducing the precursor molecules that can react to form the target molecule.
- Functional group chemistry determines reaction conversions in synthetic routes.
 Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
