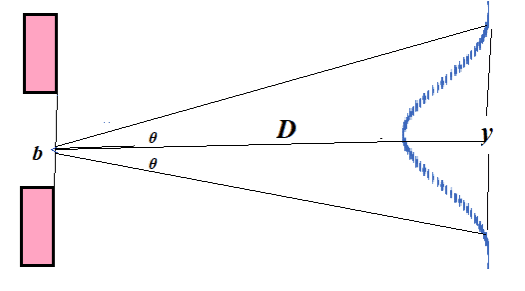
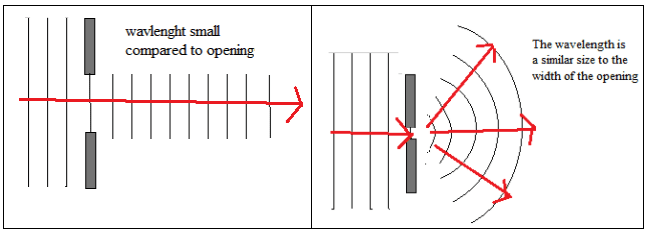
- Diffraction is the spreading of a wave as it goes through an opening or passes an obstacle. Diffraction is a property that characterises wave behaviour.
- Consider waves of wavelength $\lambda$ from the top and the middle of the rectangular slit. moving towards the right with a slit of width $b$. The path difference is $½~b\sin \theta$.
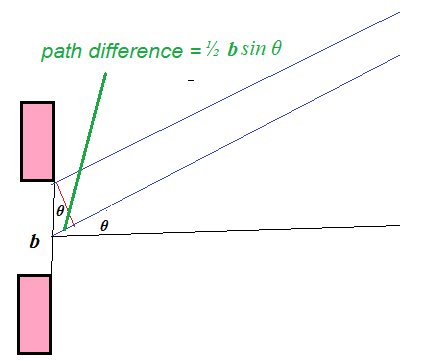
- As the angle is very small (in radians), this path difference is approximately $½~b~\theta$
- If this path difference is half a wavelength there is destructive interference and there is a minimum at a diffraction angle $\theta: \theta=\lambda$
$½~b~\theta = ½~\lambda$
$b~\theta=\lambda$ - Considering other waves below the top and just below the middle of the slit can apply the same conditions to deduce the same general result: $\theta=\lambda / b$
- When $\theta=0$ the waves arrive in phase and there is constructive interference
- The intensity of the wave varies as a function of the angle $\theta$ as shown in the graph.
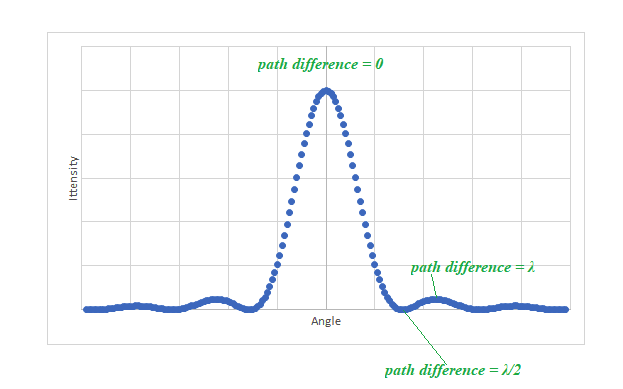
- There is non-zero intensity even when $\theta \neq 0$, as the wave diffracts.
- Maxima occur when there is constructive interference with a path difference of $n \lambda$
- Minima occur when there is destructive interference with a path difference of $(2 n+1) / 2 ~\lambda$
 Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA