The degree of a polynomial is the largest exponent seen in the polynomial. For example, the degree of $f(x) = 2x^5+4 x^3$ $−$ $7x^2+2x−1$ is $5$.
A rational function is of the form $f(x) = \dfrac{p(x)}{q(x)}$ where both $p(x)$ and $q(x)$ are polynomials.
Horizontal Asymptotes: A horizontal asymptote is an equation of a line in which the function will approach over time. In other words, the horizontal asymptote of a function of the form:
$f(x)=\dfrac{p(x)}{q(x)}$ is the line $y=k$ as $x\rightarrow \pm \infty$
Case 1: The degree of the numerator is less than the degree of the denominator. If this is the case, the equation of the horizontal asymptote is $y=0$.
Case 2: The degree of the numerator is equal to the degree of the denominator. If this is the case, the equation of the horizontal asymptote is always the leading coefficient of the numerator divided by the leading coefficient of the denominator.
Case 3: The degree of the numerator is greater than the degree of the denominator. If this is the case, there is no horizontal asymptote as the function will tend towards positive or negative infinity over time.
Example 1: What is the equation of the horizontal asymptote of the function:
$f(x)=\dfrac{−4x^2 − x + 1}{3x^2 + 8}$
Explanation: The degree of the numerator is $2$ and the degree of the denominator is $2$. This is an example of Case $2$. Therefore the equation of the horizontal asymptote is $y=−\dfrac{4}{3}$. This can be seen on the TI-84 CE graphing calculator:
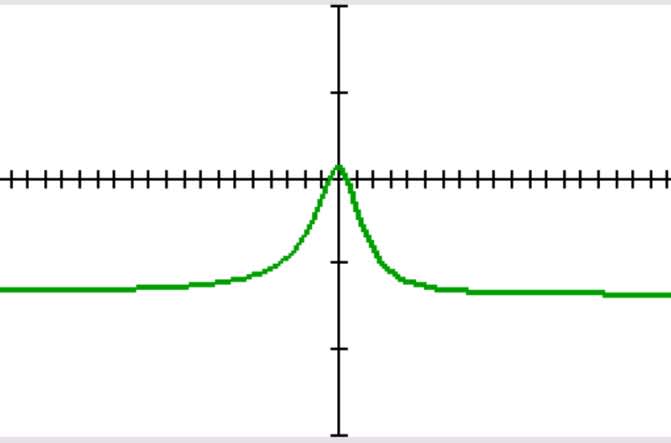
Thus, as $x\rightarrow\pm\infty$, $y\rightarrow−\dfrac{4}{3}$. Thus, the horizontal asymptote is $y=−\dfrac{4}{3}$.
Vertical Asymptotes: A vertical asymptote is an equation of a vertical line in which the function cannot cross. Algebraically, this is division by zero. Graphically this is where the function is not continuous.
Therefore, consider the function $f(x)=\dfrac{p(x)}{q(x)}$. A vertical asymptote occurs where $q(x)=0$.
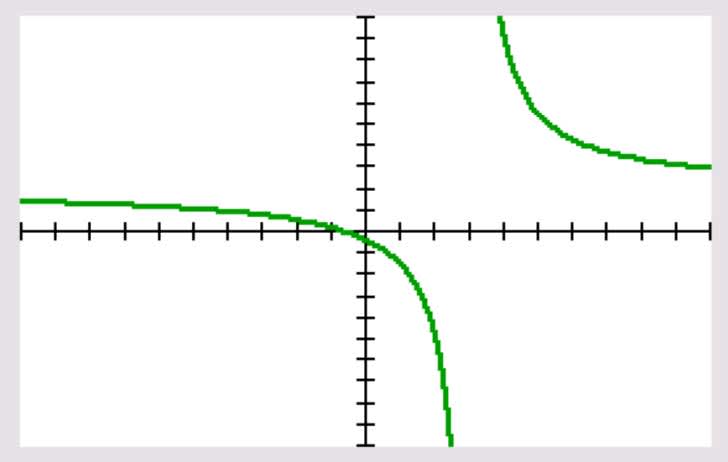
Example 2: Determine the equation of the vertical asymptote of the function:
$f(x)=\dfrac{2x+1}{x−3}$
Explanation: A vertical asymptote occurs where $q(x)=0$. This is where $x−3=0$. Therefore, the equation of the vertical asymptote is $x=3$. We can see this using the graphing calculator:
 Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
