Have you ever wondered what city planners do for a living? When trying to build and develop a city, many factors must be considered. How many schools should be built? How many hospitals or police stations should be constructed? A more important question could be not how many, but where should they be built in the city? After all, it wouldn’t make much sense to have $2$ hospitals next to each other. Emergencies will happen all over the city. It would be beneficial for the community to have the hospitals spread out so patients can receive medical care as soon as possible. This chapter will explore one way of determining where these facilities should be built. First, we must determine how to find a perpendicular bisector of a line.
Example 1: Determine the equation of the perpendicular bisector to the line that connects the points $(2,4)$ and $(6,10)$.
Explanation: Since we are looking for a bisector, we must first find the midpoint of the line connecting these points. Using the midpoint formula, the midpoint is $\left(\dfrac{2+6}{2}, \dfrac{4+10}{2}\right)=(4,7)$. Since the line we are looking for is perpendicular to the given line, the slopes are negative reciprocals of each other. The slope of the line connecting $(2,4)$ and $(6,10)$ is $m=\dfrac{10−4}{6−2}=\dfrac{3}{2}$. Thus the slope of the perpendicular bisector will be $−\dfrac{2}{3}$. Since this line travels through $(4,7)$ then the equation of the perpendicular bisector is $y−7=−\dfrac{2}{3}(x−4)$ or $y=−\dfrac{2}{3}x+\dfrac{29}{3}$.
Definition: A Voronoi diagram is a partition of a plane into regions, or cells, close to each of a given set of objects. In other words, each cell contains all the points that are closest to that object in the cell. An example is shown below:
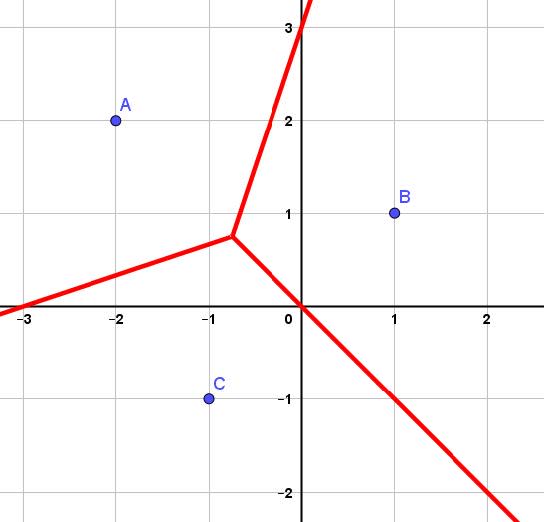
In this image the region is partitioned into $3$ cells with all other points in each region closest to either point $\rm A$, $\rm B$, or $\rm C$. For example, the point $(−1,1)$ is closest to point $\rm A$, the point $(0,2)$ is closest to point $\rm B$, etc. These boundaries are the perpendicular bisectors of the line connecting the points.
 Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
