Conservation of linear momentum is a law that is never broken.
- Momentum $\bf (p)$ is the product of the mass $\rm (m)$ and the velocity $\rm (v)$ of a body: $p = mv$.
- $p$ is a vector with the same direction as the velocity $v$.
- The unit of momentum is $\rm N$ s or $\rm kg~ ms^{-1}$.
- The kinetic energy (EK) is related to the momentum: $\mathrm{E_K} = p^2/2m$
- Newton’s second law in terms of momentum is $\mathrm{F_{net}} = \Delta p/\Delta t$.
This is the most general expression of the law as it can be applied when the mass varies. It reduces to Fnet = ma, for constant mass: $\mathrm F_{net} = \Delta p/\Delta t = m \Delta v/\Delta t = ma$. - Impulse is the product of the force on the body $\rm (F)$ and the time interval $\Delta t$ for which the force is acting. $\bf Impulse = F\Delta t$
- Impulse is a vector with the same direction as the force $\rm F$.
- Impulse equals the change in momentum of a body: $\mathrm{F_{net}} \Delta t = \Delta p$.
- Impulse is the area under the curve in a graph of $\bf F$ against $t$.
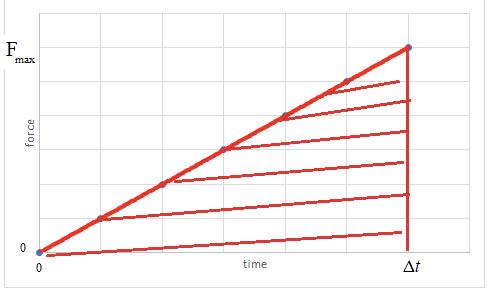
As the force is not constant:
$\rm Impulse = \text{average force}$ $\Delta t = ½ ~\mathrm{F_{max}} \Delta t =$ Area of red triangle. - The Conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of the system is constant when the resultant (net) external force on a system is zero.
- The law follows from Newton’s second law:
Let a system have total momentum $p$.
$\mathrm{F_{net}} = \Delta p/\Delta t$
If the net external force on the system is zero. $\bf F_{net} = 0$, it follows that $\Delta p = 0$: the total momentum stays constant. - Kinetic energy and momentum are conserved in an elastic collision.
When two objects with the same mass collide elastically the objects swop velocities.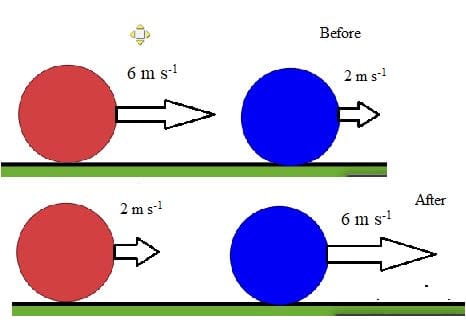
- More generally for an elastic collision, the relative velocity of approach is equals and opposite to the relative velocity of separation.
- When only momentum is conserved the collision is inelastic. Examples include collisions when objects stick together and explosions.
 Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
