The acid–base concept can be extended to reactions that do not involve proton transfer.
- A Brønsted–Lowry base accepts protons by donating a pair of lone pars to the proton. This idea is generalised in the Lewis definition of an acid and base.
- A Lewis base is a lone pair donor and a Lewis acid is a lone pair acceptor.
- A Lewis acid base reaction results in the formation of a coordinate bond.
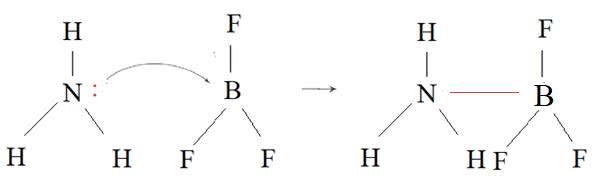
$\rm NH_3$ is a Lewis base and $\rm BF_3$ is a Lewis acid.
- A nucleophile is an electron-rich species that donates an electron pair (generally to a carbon atom) – it is a Lewis base.
- An electrophile is an electron-deficient species that accepts an electron pair (generally from a carbon atom) – it is a Lewis acid.
 Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
