Covalent compounds form by the sharing of electrons.
Covalent Bonds
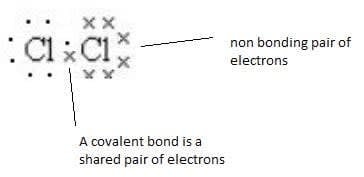
- A covalent bond is the electrostatic attraction between a pair of electrons and positively charged nuclei.
- A molecule is a group of atoms held together by covalent bonds.
- A Lewis structure shows the outer electrons in a structure.
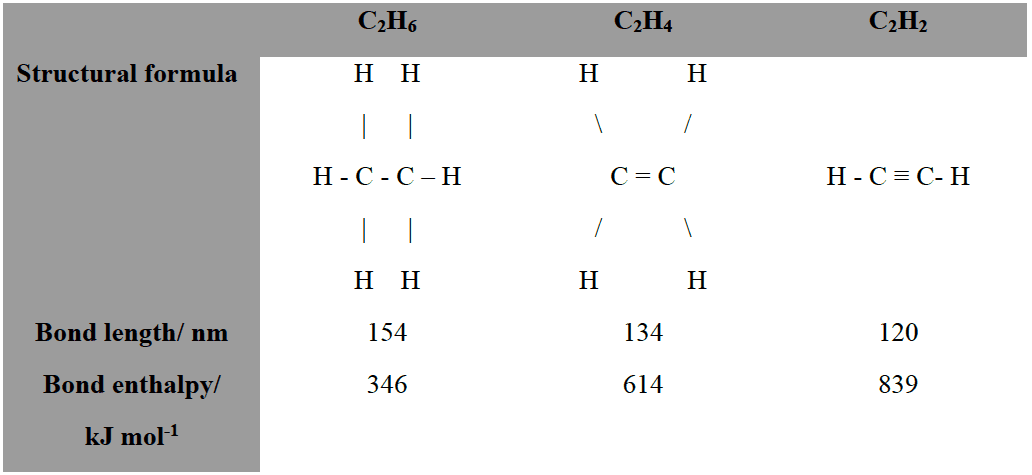
- A double bond is formed when there two atoms share two pairs of electrons and a triple bond is formed when two atoms share three pairs of electrons.
- The bond enthalpy increases with the number of bonds, the bond strength decreases with the number of bonds: triple bonds are generally shorter than double bonds which are shorter than single bonds. The greater the number of bonding electrons the closer the bonding atoms are attracted towards each other.
Coordinate Bonds
- A coordinate bond is formed when one of the atoms supplies both electrons of the shared pair of a covalent bond. For example, one of the bonds in the triple bond of carbon monoxide originates from the sharing of two electron which both originate from oxygen.

The ammonium ion $\rm NH^{4+}$ is formed when a proton $\rm H^+$ forms a coordinate bond with nitrogen by sharing the non-bonding pair of the ammonia molecule:
$\rm H^+ +: NH_3 \rightarrow [NH_4]^+$
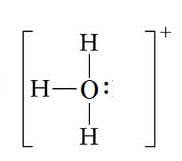
The $\rm H_3O^+$ ion is formed in a similar way by a proton combinig with a water molecule:
There is no physical difference between a normal covalent bond and a coordinated bond.
$\rm NH^{4+}$ and $\rm H_3O^+$ both contain a coordinate bond.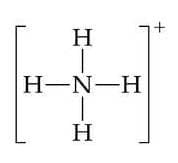
Electronegativity and Bond Polarity
- Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom in a molecule to attract a pair of shared electrons towards itself. Florine is the most electronegative element as it has a small atomic radius and a large effective nuclear charge. Francium and caesium are the least electronegative elements as they have a large atomic radius and a small effective nuclear charge.
- The difference in electronegativities of two atoms in a covalent bond gives an indication of the bond’s polarity.
- Hydrogen fluoride is a polar molecule as $\rm F$ is more electronegative than $\rm H$. polar covalent molecules have partial charges $\rm X^{\delta +}Y^{\delta -}$.
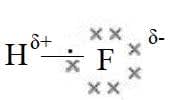
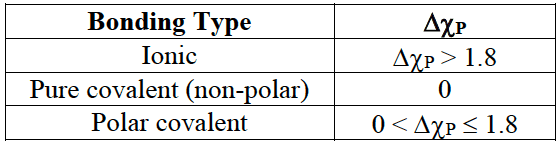
- Ionic and covalent bonding are two extremes as many substances show intermediate character. The nature of the bonding can be related to bond polarity and the difference in electronegativity values $\rm (\Delta\chi_P)$ of the bonded atoms.
 Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
