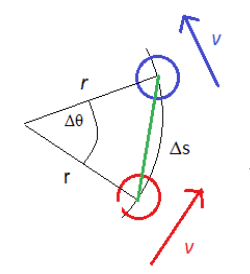
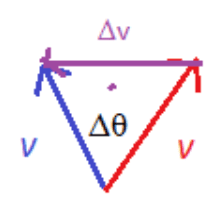
When a force is at right angles to a body’s velocity circular motion can occur.
Circular motion at constant speed: period, frequency, angular displacement and angular velocity.
- The velocity has the same magnitude but changes direction. In time $\Delta t$ the body moves, and the radius moves through an angle $\Delta \theta$.
- The angular velocity $(\omega)$ is the angle swept out by per unit time. The unit of angular velocity is the radian $s^{−1}$.
$\omega = \Delta \theta/\Delta t$ - The time period $\rm (T)$ is the time taken to complete one circle. The unit of the time period is the second:
$\omega = 2\pi/\rm T$ - The frequency is the number of complete revolutions per unit time (e.g. the second).
- $f = 1/\mathrm T$
- $\omega = 2\pi f$
- In a time, $\rm T$, the body completes one full cycle.
- $\text{distance} = 2\pi r$
- $v = 2\pi r/\rm T$ and $v = \omega r$
 Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA