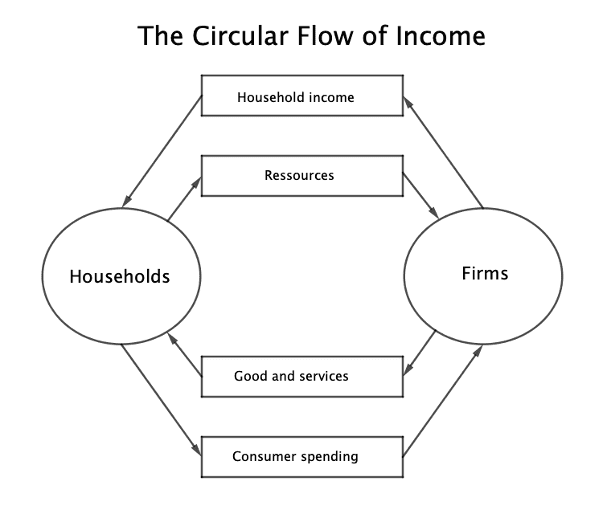
The role of households and firms
Measurement of economic activity
- GDP, which stands for Gross Domestic Product, measures the value of economic activity within a country.
- GNP, which stands for Gross National Product, is the total value of all the final products and services produced by a country during a specific period.
- GNI, which stands for Gross National Income, measures the level of wealth of the people of the country when all possible sources of income are considered.
Variations of economic activity
The four types of economic activity are:
- Producing: production of goods and services
- Providing: distribution of goods and services
- Purchasing: consumption of goods and services
- Selling: resource management
Symbols used in macroeconomics
- Exports (X)
- Government spending (G)
- Household spending (C)
- Imports (M)
- Investment (I)
- National income or output (Y)
- National spending (E)
- Savings (S)
- Taxation (T)
Equilibrium
Equilibrium occurs when:
$$S + T + M = I + G + X$$
In other words:
$$\text{Savings + Taxation + Imports}$$$$\text{= Investment + Government spending + Exports}$$
Aggregate demand
Aggregate demand, denoted Y is defined by:
$$Y=C+I+G+(X-M)$$
Where (X – M) is the difference between Exports and Imports
In other words:
$$\text{Aggregate demand = Household spending } $$$$ \text{+ Investment + Government spending }$$$$\text{+ (Exports – Imports)}$$
John Maynard Keynes’ theory
John Maynard Keynes (1883-1946) is a British economist, financier and journalist. He known for his work “The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money” published in 1935-1936.
He stated that consumption is increasing, but at a slower rate than the increase in income, because people are not spending all their money but also saving some of it.
 Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA