Market
The market has the following characteristics:
- Private property: Most goods and services are privately owned
- Freedom of choice: Owners are free to produce, sell, buy goods and services in a competitive market
- Motive of self-interest: Both consumers and producers pursue their self-interest
- Competition: Demand and supply determine prices. The more the demand increases, the more the prices increase (law of demand)
- Limited government: The government ensures that the markets are stable, fair, open, working, and safe
Demand
Demand depends on:
- Product price
- Prices of related goods
- Consumer income
- Consumer tastes
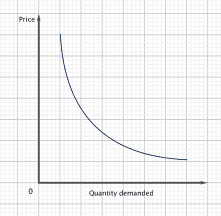
The demand curve:
It is a curve that shows the relationship between price and quantity demanded by consumers. As the price of a good decreases the quantity of demands increases.
Shifting demand curve and type of good:
- Substitute or alternative good: good that can be used in place of another
- Inferior good: good that becomes less desirable as consumer income rises
- Normal good: good that becomes more desirable as consumer income rises
Supply
Supply depends on:
- Price of a good
- Prices of other goods
- Cost of production
- Technical progress
- Governments’ policies: government taxes and subsidies
- Transportation condition
- Goal of the firm
- Expectation about the future regarding price
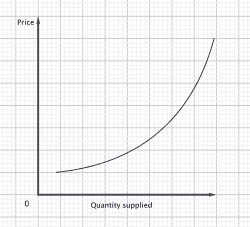
The supply curve:
It is a curve that shows the relationship between price and quantity supplied by producers.
As the price of a good increases the quantity of supplies increases. In other words, when prices rise, producers increase supply.
Economic Profits:
Profit = Total revenue – Total cost
Economic profit = Total revenue – Opportunity cost
Accounting profit = Total revenue – Explicit cost
 Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA