Measuring inequality
- GDP, which stands for Gross Domestic Product, measures the value of economic activity within a country.
- GNI, which stands for Gross National Income, measures the level of wealth of the people of the country when all possible sources of income are considered.
- GNI per capita.
- HDI, which stands for Human Development Index, measures the standards living of a country. The standards living are, for instance, life expectancy at birth, mean years of schooling, etc.
- IHDI, which stands for Inequality-adjusted Human Development Index, comprehends the repercussion of inequality that an average person faces in the economy.
- MPI, which stands for Global Multidimensional Poverty Index, shows how poverty touches individuals in the economy.
Representing inequality
- The Lorenz curve
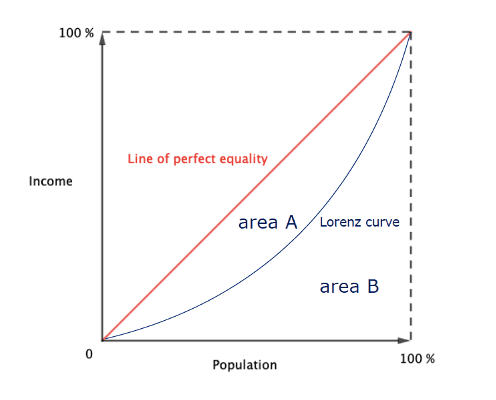
- The Gini coefficient $\rm G=\dfrac{\text { area } A}{\operatorname{area}(A+B)}$
- $\rm G$ measures the inequality between values of a frequency distribution, mostly income levels. Gini coefficient is a measure of inequality of income or wealth within a country.
- $\rm G$ is included between $0$ and $1$ and is expressed in percent.
- Interpretation: the inequality is all the stronger as the Gini coefficient is high (close to $1$).
Reducing inequality
Governments interventions to tackle inequalities and poverty:
- Progressive taxation
- Social expenditures
- Health care expenditures
- Minimum wage
- Setting limits for banks
 Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
