Full employment of labor
In principle, full employment is achieved when the economy is at the production possibility frontier.
Two types of unemployment:
- Structural unemployment: happens when an industry is in decline
- Frictional unemployment: concerns those who seek employment after a short-term job
Price stability
- There is price stability when average prices remain constant
- CPI, stands for Consumer Price Index
- Inflation rate: percentage increase in average prices in the economy within a year
$$\Delta_{\%}=\frac{\text { Ending cost }-\text { Starting cost }}{\text { Starting cost }} \times 100$$
- Be careful: Inflation only occurs if average price levels rise. Inflation is not about the rise in price of a single good.
- Inflation weakens the market’s capacity to allocate resources. It can lead to confusion that devastate markets in the event of hyperinflation.
- Governments benefit from inflation:
- When they borrow
- Fiscal drag: income tax revenues rise with inflation and stagnant tax rates
Sustainable economy growth
Fisher equation:
$$i \approx r+\pi$$
where:
$i$ is the nominal interest rate $r$ is the real interest rate
$\pi$ is the inflation rate
Balance of payments equilibrium
- If exports > imports $\Rightarrow$ balance of payments surplus (trade surplus)
- If exports < imports $\Leftarrow$ balance of payments deficit (trade deficit)
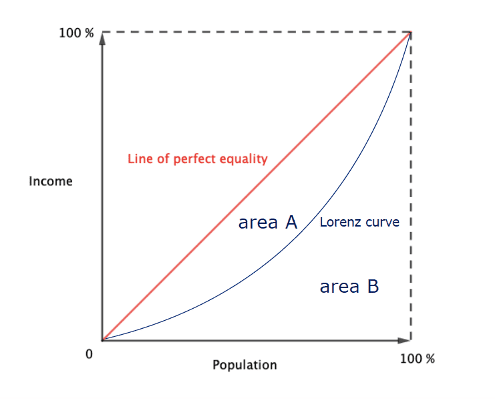
The distribution of income
- The Lorenz curve
- The Gini coefficient
$$\rm G=\frac{\text { area } A}{\operatorname{area}(A+B)}$$
- $\rm G$ measures the inequality between values of a frequency distribution, mostly income levels. Gini coefficient is a measure of inequality of income or wealth within a country.
- $\rm G$ is included between $0$ and $1$ and is expressed in percent.
- Interpretation: the inequality is all the stronger as the Gini coefficient is high (close to $1$).
 Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA