Increased industrialization has led to greater production of nitrogen and sulfur oxides leading to acid rain, which is damaging our environment. These problems can be reduced through collaboration with national and intergovernmental organizations.
- Normal rainwater is acidic due to dissolved $\rm CO_2$ which forms carbonic acid.
$\rm H_2O(l) + CO_2(aq) \rightleftharpoons H_2CO_3(aq)$ $\rm \rightleftharpoons H^+(aq) + HCO^– _3(aq)$ - Acid deposition is the process by which acidic substances leave the atmosphere and return to Earth. It includes all forms of precipitation from the atmosphere as gas or solid that have a $\rm pH < 5.6$.
- Acid deposition results from oxides of nitrogen and sulfur: $\rm HNO_3$, $\rm HNO_2$, $\rm H_2SO_4$, and $\rm H_2SO_3$ dissolved in water.
- Sulfur oxides are generally produced from the burning of fossil fuels, especially coal. The reactions produce $\rm SO_2$ that is oxidized further to $\rm SO_3$. Reactions with water form $\rm H_2SO_3$ and $\rm H_2SO_4$.
$\rm SO_2(g) + H_2O(l) \rightleftharpoons H_2SO_3(aq)$
$\rm SO_3(g) + H_2O(l) \rightleftharpoons H_2SO_4(aq)$ - Nitrogen oxides are produced mostly from internal combustion engines. $\rm NO$ is the primary pollutant which is oxidized to $\rm NO_2$, which then dissolves in water to form $\rm HNO_3$ and $\rm HNO_2$.
$\rm 2NO_2(g) + H_2O(l)$ $\rm \rightleftharpoons HNO_2(aq) + HNO_3(aq)$
Sources of nitrogen and sulfur oxides.
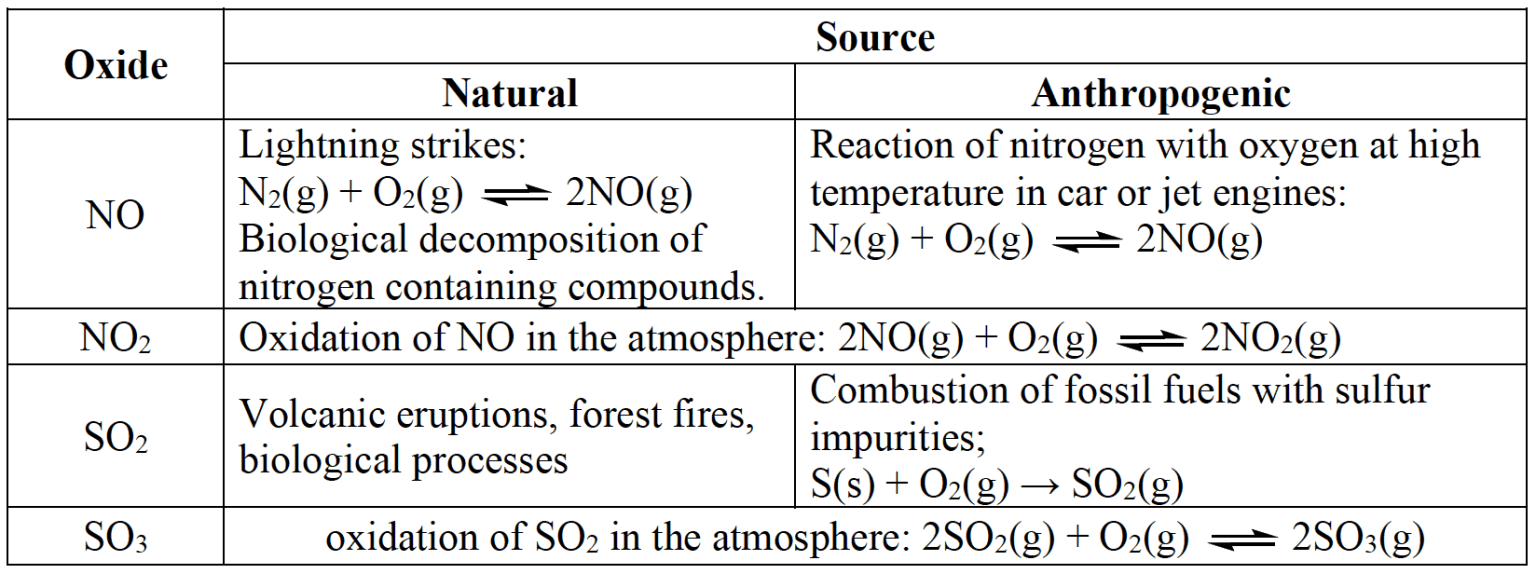
- The formation of $\rm HNO_2(aq)$ from $\rm NO(g)$ and $\rm HNO_3$ from $\rm NO_2$ are photooxidation reactions which occur during sunlight involving a reactive free radical with unpaired electrons.
- The hydroxyl radical $\rm \bullet ~OH$ is formed by the reaction between water and ozone:
$\rm H_2O(g)+O_3(g)\rightarrow 2HO\bullet (g)+O_2$
The hydroxyl radical reacts with nitrogen and sulfur oxides;
$\rm NO + \bullet ~OH \rightarrow HNO_2$
$\rm NO_2 + \bullet ~OH \rightarrow HNO_3$
$\rm SO_2 + \bullet ~OH \rightarrow HOSO_2~\bullet$ $\rm HOSO_2\bullet + O_2$ $\rm \rightarrow HO_2\bullet + SO_3$ - Acid deposition damages limestone and metallic structures. The reactions are the same as those covered in section $8.2$.
- Acid deposition also harms plant and animal life and pollutes lakes.
- Responses to acid deposition include removing sulfur from fuels before combustion (hydrodesulfurization) and/or sulfur dioxide from flue gases. Nitrogen oxides emissions from vehicles are reduced by catalytic converters and by carrying out combustion at lower temperatures.
 Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
Nouveau ! Découvrez Nomad'IA : le savoir de nos 400 profs + la magie de l'IA
